Coexistence of distinct intramolecular electron transfer pathways in polyoxometalate based molecular triads†
Abstract
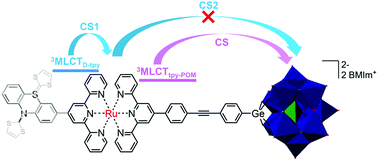
Polyoxometalate (POM)-associated charge-separated states, formed by the photoinduced oxidation of a covalently attached photosensitizer and reduction of the POM, have attracted much attention due to the remarkable catalytic properties of the reduced POMs. However, short lifetimes of the POM-associated charge-separated state, which in some cases lead to the backward electron transfer being more rapid than the formation of the charge-separated state itself, are generally observed. Recently, we reported on the first example of a relative long-lived (τ = 470 ns) charge-separated state in a Ru(II) bis(terpyridine)-POM molecular dyad. In this manuscript, further studies on extended molecular structures – two molecular triads – which contain an additional electron donor, phenothiazine (PTZ) or π-extended tetrathiafulvalene (exTTF), are discussed. We show that the excitation of the photosensitizer leads to the population of two distinct MLCT states, which differ in the distribution of excess electron density on the two distinct tpy ligands. These two MLCT states decay separately and, thus, constitute the starting points for distinct intramolecular electron-transfer pathways leading to the simultaneous population of two partially charge-separated states, i.e. PTZ˙+-Ru(tpy)2˙−-POM and PTZ-RuIII(tpy)2-POM˙−. These independent decay pathways are unaffected by the choice of the electron donor. Thus, the initial charge distribution within the coordination environment of the photocenter determines the nature of the subsequent (partially) charge separated state that is formed in the triads. These results might open new avenues to design molecular interfaces, in which the directionality of electron transfer can be tuned by the choice of initial excitation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...