Effects of oxygen chemical potential on the anisotropy of the adsorption properties of Zr surfaces†
Abstract
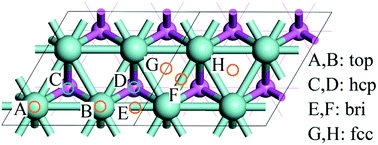
The anisotropy of metal oxidation is a fundamental issue, and the oxidation of Zr surfaces also attracts much attention due to the application of Zr alloys as cladding materials for nuclear fuels in nuclear power plants. In this study, we systematically investigate the diagram of O adsorption on low Miller index Zr surfaces by using first-principles calculations based on density functional theory calculations. We find that O adsorption on the basal surface, Zr(0001), is more favourable than that on the prism surfaces, Zr(11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 0) and Zr(10
0) and Zr(10![[1 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0031_0304.gif) 0), under strong O-reducing conditions, while O adsorption on the prism surface is more favourable than that of the basal surface under weak O-reducing conditions and the O-rich conditions. Our findings reveal that the anisotropy of adsorption properties of O on the Zr surfaces is dependent on the O chemical potential in the environment. Furthermore, the ability of the prism for O adsorption is stronger than that of the basal surface under the O-rich condition, which is consistent with the experimental observation that the oxidation of the prism Zr surface is easier than that of the basal surface. Systematic surveys show the adsorption ability of the surface under strong O-reducing conditions is determined by the low coordination numbers of surface atoms and surface geometrical structures, while the adsorption ability of the surface under weak O-reducing conditions and O-rich conditions is only determined by the low coordination number of surface atoms. These results can provide an atomic scale understanding of the initial oxidation of Zr surfaces, which inevitably affects the growth of protective passivation layers that play critical roles in the corrosion resistance of Zr cladding materials.
0), under strong O-reducing conditions, while O adsorption on the prism surface is more favourable than that of the basal surface under weak O-reducing conditions and the O-rich conditions. Our findings reveal that the anisotropy of adsorption properties of O on the Zr surfaces is dependent on the O chemical potential in the environment. Furthermore, the ability of the prism for O adsorption is stronger than that of the basal surface under the O-rich condition, which is consistent with the experimental observation that the oxidation of the prism Zr surface is easier than that of the basal surface. Systematic surveys show the adsorption ability of the surface under strong O-reducing conditions is determined by the low coordination numbers of surface atoms and surface geometrical structures, while the adsorption ability of the surface under weak O-reducing conditions and O-rich conditions is only determined by the low coordination number of surface atoms. These results can provide an atomic scale understanding of the initial oxidation of Zr surfaces, which inevitably affects the growth of protective passivation layers that play critical roles in the corrosion resistance of Zr cladding materials.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2018 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...