Energy dispersive spectrometry and first principles studies on the oxidation of pentlandite†
Abstract
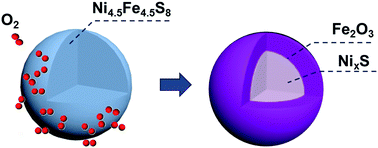
Experimental and computational studies were carried out to investigate the oxidation of pentlandite (Fe4.5Ni4.5S8). The oxidation product was first analyzed by energy dispersive spectrometry to reveal the elemental distribution at the cross section. Our experimental study shows that the Fe atoms in pentlandite migrated to the surface and were preferentially oxidized to form a thin layer of Fe2O3, whereas the Ni atoms remained at the center of the grain. Furthermore, density functional theory calculations were performed to investigate the adsorption and diffusion of atomic oxygen as well as the adsorption and dissociation of molecular oxygen on the (001) and (010) surfaces of pentlandite. From the calculated adsorption energies of atomic oxygen at the different sites of the (001) and (010) surfaces, we found that oxidation of the Fe sites was preferable to that of the Ni sites when exposed to an oxidizing atmosphere. For molecular oxygen adsorption on the surfaces of pentlandite, the bridge sites (Fe–Ni and Fe–Fe) were found to be the most favorable adsorption sites. The dissociative adsorption of O2 is thermodynamically more favorable than the molecular adsorption. Calculated dissociation barriers show that the oxidation is feasible during high temperature roasting.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...