The gelation influence on diffusion and conductivity enhancement effect in renewable ionic gels based on a LMWG†
Abstract
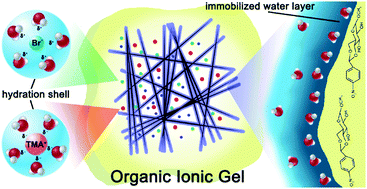
This paper reports the interdisciplinary study on molecular dynamics, ionic interactions and electrical conductivity in a quaternary ammonium salt (TMABr) ionogel based on a low molecular weight gelator (LMWG) in a wide range of electrolyte molar concentrations. The thermal scanning conductometry (TSC) was used to investigate the electric properties of the ionogels. The prepared TMABr/H2O/LMWG ionogel exhibits better ion transport properties than the dissociated TMA+ cation in solution. The enhanced ionic conductivity effect (EICE) was observed in the concentration range of the TMABr salt up to 1 M. To investigate the transport properties of the TMA+ cation and solvent molecules in the gel and sol phase, the NMR diffusiometry method was used. The field-cycling relaxometry method (FFC NMR) was applied to study the local motions of the electrolyte at the surface of the gelator matrix. On the basis of the obtained data, the higher ionic conductivity observed in the gel phase has been related to the microstructure of the gel matrix. The possible explanation for the origin of this effect has been given. The investigated system is a thermally reversible physical gel, all registered data were reproducible upon transforming the sample from gel to sol and back to the gel state, confirming the enhancement effect as a permanent property of the investigated ionogels. Therefore, the EICE has been proposed to be used as an internal sensor to monitor the condition of the ionogel phase, thus making them smart materials.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...