Enhanced photocatalytic properties of ZnO nanorods by electrostatic self-assembly with reduced graphene oxide†
Abstract
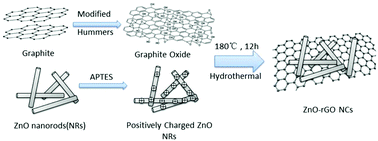
A series of ZnO nanorod (NR)-reduced graphene oxide (rGO) nanocomposites (NCs) (i.e., ZnO–rGO NCs) with varying rGO loadings were fabricated by electrostatic self-assembly of positively charged ZnO NRs with negatively charged graphene oxide (GO), followed by the hydrothermal reduction of GO to rGO. When compared with bare ZnO NRs, ZnO-5% rGO exhibited significant photoactivity 6 times higher in the photodegradation of rhodamine B (RhB), and 2 times higher than ZnO-5% rGO(H) synthesized by hard integration of GO and ZnO NRs. In the same manner, ZnO-5% rGO exhibited a significant photoactivity 3 times higher in photodegrading phenol, which is 2 times higher than ZnO-5% rGO(H). Furthermore, the adsorption properties of ZnO–rGO NCs towards RhB and phenol were significantly different as a result of the opposite charges of the two pollutants in aqueous solution, which also led to the formation of different key free radicals during the degradation reaction. Based on various characterization techniques, it is concluded that the enhanced photoactivity and photostability of ZnO-5% rGO originated from the synergistic effects between ZnO NRs and rGO nanosheets including higher specific surface area, enhanced photogenerated carrier separation, and strengthened protection effects from intimate rGO coupling. However, these synergistic effects were weaker in ZnO-5% rGO(H) which reflects the key importance of surface charge modification in producing a well-contacted interface.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...