The effect of water on the physicochemical properties of an ethylene glycol and choline chloride mixture containing Cu2+ ions: electrochemical results and dynamic molecular simulation approach†
Abstract
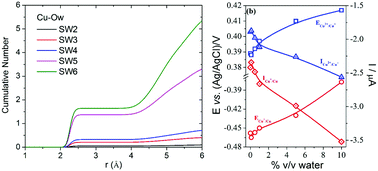
The effect of water on the physicochemical properties of an ethylene glycol and choline chloride mixture containing Cu2+ ions was investigated by electrochemical techniques and molecular dynamics simulation. The experiments and computational calculations were carried out by increasing the water content from 0 up to 10% (v/v). The cyclic voltammetry and chronopotentiometry techniques showed that the diffusion coefficient of Cu2+ ions increased and that the peak potentials for both the Cu2+/Cu+ and Cu+/Cu redox couples shifted towards more positive potentials with the increase in the water content in the solution. The molecular dynamics simulation indicated that the water molecules replaced the ethylene glycol molecules that were coordinated with Cu2+ ions, while the interactions between Cu2+ and Cl− ions were not influenced by the presence of water.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...