Probing electron transfer between hemin and riboflavin using a combination of analytical approaches and theoretical calculations†
Abstract
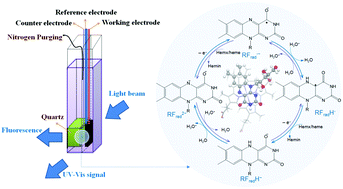
Extracellular electron transfer (EET) occurs from outer-membrane proteins to electron acceptors. Heme(II) is the active center of outer-membrane proteins and delivers electrons to acceptors or mediators such as riboflavin, a redox active chromophore present in organisms. However, the EET mechanism via mediators, especially the electron transfer process from outer-membrane proteins to mediators, has not been well documented yet. In this work, the mechanism behind the electron transfer from heme(II) to riboflavin is investigated by using in situ ultraviolet visible and fluorescence spectroelectrochemical analysis, which provides the information regarding the structural change and electrochemical characteristics of species in the electron transfer process. It is found that hemin(III), the oxidized form of heme(II), is electrolyzed to an intermediate “hemx(II)” without structural changes, and is then transformed to heme(II) by conjugating with riboflavin and its radicals. Heme(II) is able to activate riboflavin reduction via a two-electron two-proton pathway in aqueous solution. The mechanisms proposed on the basis of experimental results are further confirmed by density functional theory calculations. The results about the electron transfer from hemx(II) (or heme(II)) to riboflavin are useful not only for understanding the EET mechanisms, but also for maximizing the role of riboflavin in biogeochemical cycling and environmental bioremediation.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...