Design and construction of a bifunctional magnetically recyclable 3D CoMn2O4/CF hybrid as an adsorptive photocatalyst for the effective removal of contaminants
Abstract
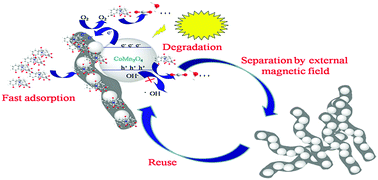
Herein, a magnetic microsphere CoMn2O4 (MS-CoMn2O4) with a 3D architecture was constructed directly on cellulose fiber (CF) substrates from wastepaper by a solvothermal synthesis method with further calcination treatment. The designed hybrid shows excellent dual functions including rapid catalytic oxidation of tetracycline (TC)/methylene blue (MB) and a high adsorption capacity. What's more, the hybrid is easily recycled using an external magnetic field. In comparison with that of pure MS-CoMn2O4, the enhanced adsorption ability and photocatalytic activity of MS-CoMn2O4/CFs can mainly be attributed to the introduced cellulose fiber supporter in the hybrid system. MS-CoMn2O4 incorporated CFs can improve the efficient separation of photogenerated electron–hole pairs and the transport pathway of electrons. More importantly, introduction of CFs can help to enrich and further improve the degradation efficiency of organic contaminants. The possible mechanism for the enhancement of the photocatalytic activity has been elucidated in detail. The reusability analysis revealed that the MS-CoMn2O4/CF hybrid exhibited superb cycling stability after 5 cycles. This study provides novel insights into the design and construction of high capacity sorbents as strongly adsorptive photocatalysts to perform catalytic degradation of organic contaminants.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...