Non-noble metal plasmonic photocatalysis in semimetal bismuth films for photocatalytic NO oxidation†
Abstract
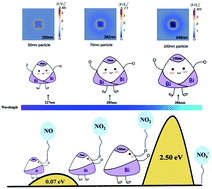
Recently, non-noble metals with plasmonic properties have attracted great attention due to their potential applications in photocatalytic solar-energy conversion. However, in contrast to the well-studied plasmonic noble metals (mainly Au and Ag), which have distinct absorption peaks, the understanding of light absorption and the photocatalytic reaction mechanism of non-noble metals is far less. In this study, semimetal bismuth films are deposited on fluorine-doped tin oxide substrates by a dc magnetron sputtering method. Both theoretical calculation and UV-vis absorption spectra confirm that the field enhancement and location of plasmonic resonance peaks are strongly correlated with the size of Bi particles. Through tuning the sputtering power, for the first time, four distinct absorption peaks are observed over isolated Bi particles. Moreover, it is found that the energy barrier for the conversion of NO into NO2 over Bi is even lower than that with Au nanoclusters. Thus, Bi films are highly active for photocatalytic oxidation of NO. Moreover, the low NO2 desorption energy over Bi indicates that Bi films can be the main active sites during the reaction process and that they possess good stability.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...