Controlling the ferroelectric and resistive switching properties of a BiFeO3 thin film prepared using sub-5 nm dimension nanoparticles†
Abstract
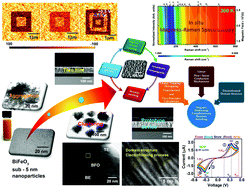
In recent years, BiFeO3 has attracted significant attention as an interesting multiferroic material in the exploration of fundamental science and development of novel applications. Our previous study (Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys.18, 2016, 25409) highlighted the interesting physicochemical features of BiFeO3 of sub-5 nm dimension. The study also accentuated the existence of weak ferroelectricity at sub-5 nm dimensions in BiFeO3. Based on this feature, we have prepared thin films using sub-5 nm BiFeO3 nanoparticles and explored various physicochemical properties of the thin film. We report that during the formation of the thin film, the nanoparticles aggregated; particularly, annihilation of their nanotwinning nature was observed. Qualitatively, the Gibbs free energy change ΔG governed the abovementioned processes. The thin film exhibited an R3c phase and enhanced Bi–O–Fe coordination as compared to the sub-5 nm nanoparticles. Raman spectroscopy under the influence of a magnetic field shows a magnetoelectric effect, spin phonon coupling, and magnetic anisotropy. We report room-temperature ferroelectric behavior in the thin film, which enhances with the application of a magnetic field; this confirms the multiferroic nature of the thin film. The thin film shows polarization switching ability at multiple voltages and read–write operation at low bias (±0.5 V). Furthermore, the thin film shows negative differential-complementary resistive switching behavior in the nano-microampere current range. We report nearly stable 1-bit operation for 102 cycles, 105 voltage pulses, and 105 s, demonstrating the paradigm device applications. The observed results thus show that the thin films prepared using sub-5 nm BiFeO3 nanoparticles are a promising candidate for future spintronics and memory applications. The reported approach can also be pertinent to explore the physicochemical properties and develop potential applications of several other nanoparticles.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...