Enhanced stability and water solubilizing capacity of water-in-oil microemulsions based on protic ionic liquids†
Abstract
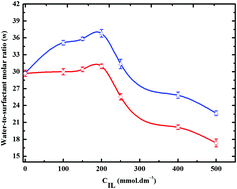
In an attempt to increase the stability and water uptake capacity of water-in-oil (W/O) microemulsions, here we study the physicochemical behavior of a series of protic ionic liquid based water/oil microemulsions, wherein solute amounts of biocompatible tetramethylguanidinium cation-based ionic liquids (ILs) are added to the aqueous phase of water-in-oil (W/O) microemulsions. FTIR and time-resolved fluorescence measurements showed an increased water uptake in these reverse micellar droplets, compared to conventional W/O microemulsions of similar compositions. Dynamic light scattering and differential scanning calorimetric measurements suggested greater thermal stability of the droplets in presence of the ILs. NMR and FTIR measurements and ab initio calculations explained these findings by showing an extended hydrogen bonding network between interfacial water and protic IL ions and strong electrostatic associations between the surfactant headgroups and IL anions. Our results pave the way for potential applications of protic ionic liquids in emulsion and microemulsion science and technology.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...