New insights into single-compound and binary adsorption of copper and lead ions on a treated sea mango shell: experimental and theoretical studies
Abstract
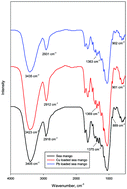
Herein, adsorption isotherms of Pb(II) and Cu(II) ions on treated sea mango fruit in both single-compound and binary systems were experimentally realized at different temperatures in the range of 30–50 °C. Experimental results show that adsorption of Pb(II) was more as compared to that of Cu(II) ions; however, for both ions, a significant reduction in the adsorption capacity was observed in the binary system as compared to that in the single-compound systems. Moreover, under all the investigated conditions, adsorption seems to be promoted by an increase in temperature. To understand and interpret the experimental evidences, the Hill and competitive Hill models developed on the basis of the grand canonical ensemble were applied for the analysis of adsorption equilibrium data. These models contain some physicochemical parameters that allow an exhaustive analysis of the dynamics of single-compound and binary adsorptions. Based on the fitting results, in particular, through the evaluation of the number of ions bonded per site (n and ni), it was found that lead and copper ions interacted by inclined and horizontal positions on treated sea mango in single-compound and binary systems, respectively. In addition, based on the same parameters, a significant interaction between ions was retrieved. A study focused on the saturation adsorption capacity in single-compound and binary systems affirmed that the adsorbent was more selective for lead than for copper. The reduction of the adsorbed capacity ratio between the binary and single-compound systems (i.e. Qb/Qs) explained and confirmed that an inhibition effect between copper and lead ions at the same receptor site occurred. Finally, based on the energetic investigations, it was deduced that the adsorption energy represented the dominant factor promoting the greater adsorption of lead than that of copper in both systems.
- This article is part of the themed collection: 2017 PCCP HOT Articles


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...