Novel multiple phosphorescence in nanostructured zinc oxide and calculations of correlated colour temperature
Abstract
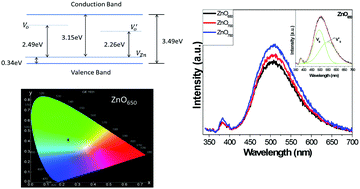
The design and development of novel and high quantum efficiency luminescent materials, such as phosphors, having tuneability in properties, have received tremendous interest among scientists. In this paper, we have achieved for the first-time multiple phosphorescence (blue and green) having a life-time of ∼10 μs in nanostructured zinc oxide that was synthesized using an easy and facile sol–gel method. Importantly, the photoluminescence (PL) intensity and the phosphorescence life-time could be tuned by controlling the annealing temperature under a reducing atmosphere. Temperature and atmosphere dependent variation of [VO] and 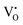 has been interpreted by the detailed thermodynamic analysis of defect chemistry, for the first time. These nanostructured zinc oxide particles being sufficiently large in size (around 160 nm) are extremely stable and expected to show photoluminescence for a longer period of time than nanorods and quantum dots. The quantum yield was found to be as high as 13–15% which is comparable to the order of magnitude of that of quantum dots. The calculated correlated colour temperature is found to be suitable for cool lighting applications.
has been interpreted by the detailed thermodynamic analysis of defect chemistry, for the first time. These nanostructured zinc oxide particles being sufficiently large in size (around 160 nm) are extremely stable and expected to show photoluminescence for a longer period of time than nanorods and quantum dots. The quantum yield was found to be as high as 13–15% which is comparable to the order of magnitude of that of quantum dots. The calculated correlated colour temperature is found to be suitable for cool lighting applications.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...