Engineering defects and photocatalytic activity of TiO2 nanoparticles by thermal treatments in NH3 and subsequent surface chemical etchings†
Abstract
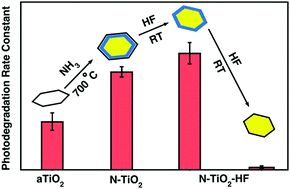
TiO2 nanoparticles with N dopants were prepared by thermal treatments in NH3 and their surface defects were controlled by post chemical etching in HF to find out the influence of the N dopants on photoactivity. The effect of N-doping is found to enhance the photoactivity of TiO2, but is strongly dependent on the degree of N-doping and the detailed distribution of nitrogen species within the TiO2 nanoparticles. In particular, the N-rich layers formed near the surface are found to contribute to the enhanced photoactivity due to the reduced band gap. But, the increase in the N concentration may induce defects that act as recombination centers and reduce the photoactivity. Subsequent chemical etching in HF confirms the existence of the substitutional N species near the surface from the observation of paramagnetic N species. But, prolonged HF treatments are found to decrease the photoactivity primarily due to the removal of the N-rich surface layers that are responsible for the enhanced photoactivity. Our results show that the photoactivity of N-doped TiO2 is strongly influenced by the type and the density of the N dopants induced by the N doping.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...