Binding modes and pathway of RHPS4 to human telomeric G-quadruplex and duplex DNA probed by all-atom molecular dynamics simulations with explicit solvent†
Abstract
RHPS4, a potent binder to human telomeric DNA G-quadruplex, shows high efficacy in tumor cell growth inhibition. However, it's preferential binding to DNA G-quadruplex over DNA duplex (about 10 fold) remains to be improved toward its clinical application. A high resolution structure of the single-stranded telomeric DNA G-quadruplexes, or B-DNA duplex, in complex with RHPS4 is not available yet, and the binding nature of this ligand to these DNA forms remains to be elusive. In this study, we carried out 40 μs molecular dynamics binding simulations with a free ligand to decipher the binding pathway of RHPS4 to a DNA duplex and three G-quadruplex folders (parallel, antiparallel and hybrid) of the human telomeric DNA sequence. The most stable binding mode identified for the duplex, parallel, antiparallel and hybrid G-quadruplexes is an intercalation, bottom stacking, top intercalation and bottom intercalation mode, respectively. The intercalation mode with similar binding strength to both the duplex and the G-quadruplexes, explains the lack of binding selectivity of RHPS4 to the G-quadruplex form. Therefore, a ligand modification that destabilizes the duplex intercalation mode but stabilizes the G-quadruplex intercalation mode will improve the binding selectivity toward G-quadruplex. The intercalation mode of RHPS4 to both the duplex and the antiparallel and the hybrid G-quadruplex follows a base flipping-insertion mechanism rather than an open-insertion mechanism. The groove binding, the side binding and the intercalation with flipping out of base were observed to be intermediate states before the full intercalation state with paired bases.
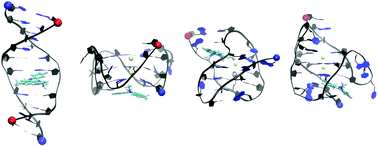


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...