Isomerization versus dissociation of phenylalanylglycyltryptophan radical cations†
Abstract
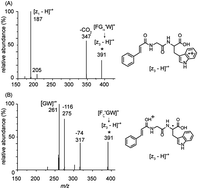
Four isomers of the radical cation of tripeptide phenylalanylglycyltryptophan, in which the initial location of the radical center is well defined, have been isolated and their collision-induced dissociation (CID) spectra examined. These ions, the π-centered [FGWπ˙]+, α-carbon- [FGα˙W]+, N-centered [FGWN˙]+ and ζ-carbon- [Fζ˙GW]+ radical cations, were generated via collision-induced dissociation (CID) of transition metal–ligand–peptide complexes, side chain fragmentation of a π-centered radical cation, homolytic cleavage of a labile nitrogen–nitrogen single bond, and laser induced dissociation of an iodinated peptide, respectively. The π-centered and tryptophan N-centered peptide radical cations produced almost identical CID spectra, despite the different locations of their initial radical sites, which indicated that interconversion between the π-centered and tryptophan N-centered radical cations is facile. By contrast, the α-carbon-glycyl radical [FGα˙W]+, and ζ-phenyl radical [Fζ˙GW]+, featured different dissociation product ions, suggesting that the interconversions among α-carbon, π-centered (or tryptophan N-centered) and ζ-carbon-radical cations have higher barriers than those to dissociation. Density functional theory calculations have been used to perform systematic mechanistic investigations on the interconversions between these isomers and to study selected fragmentation pathways for these isomeric peptide radical cations. The results showed that the energy barrier for interconversion between [FGWπ˙]+ and [FGWN˙]+ is only 31.1 kcal mol−1, much lower than the barriers to their dissociation (40.3 kcal mol−1). For the [FGWπ˙]+, [FGα˙W]+, and [Fζ˙GW]+, the barriers to interconversion are higher than those to dissociation, suggesting that interconversions among these isomers are not competitive with dissociations. The [z3 − H]˙+ ions isolated from [FGα˙W]+ and [Fζ˙GW]+ show distinctly different fragmentation patterns, indicating that the structures of these ions are different and this result is supported by the DFT calculations.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...