Molecular determinants involved in differential behaviour between soluble tissue factor and full-length tissue factor towards factor VIIa†
Abstract
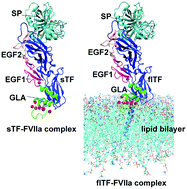
During blood-coagulation, the transmembrane protein tissue factor (TF) binds to its ligand, factor (F)VII, activating and allosterically modifying it to form a mature active binary complex (TF–FVIIa). Although the extracellular domain of TF (sTF) can bind to FVII, it fails to activate it. Binding of TF with FVIIa only partially enhances FVIIa proteolytic activity. Our previous kinetic study revealed that sTF has a lower binding capacity with FVIIa compared to membrane bound full-length (fl)TF. The reason behind this incapability of FVII activation and reduced catalytic activity remains unexplored due to the lack of an flTF crystal structure. Here we employed a comparative dynamic study between sTF–FVIIa in solution and flTF–FVIIa in a membrane system to give probable explanations for the differential behaviour of these complexes. Based on potential of mean force and interaction energy calculations, the binding affinities between sTF and FVIIa are weaker than those of the flTF–FVIIa complex. We further observed domain-wise less stability, reduced height, and thus less inter and intra-domain interaction between the sTF and FVIIa complexes. We detected higher fluctuation among the inter-atomic distances of the catalytic triad (CT) residues in sTF–FVIIa over the flTF–FVIIa complex. The flTF–FVIIa complex forms two major interactions between EGF2 and TF. We showed the enhanced activity of the flTF–FVIIa complex over the sTF–FVIIa complex, which is guided by mainly two interactions between EGF2 and TF. Due to the lack of these interactions, sTF–FVIIa somehow forms a less stable binary complex and could not react upon binding its substrates (FIX, FX). Our study, for the first time, provides a possible explanation of the distinct behaviour of the two forms of TF (sTF and flTF) towards its only ligand FVII/FVIIa.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...