Tuning the gap of lead-based halide perovskites by introducing superalkali species at the cationic sites of ABX3-type structure
Abstract
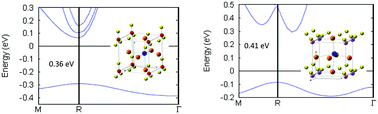
We study with scalar relativistic density functional theory (DFT) calculations the effect of changes in the ionicity of the bonding mechanism and charge donation on the structure and electronic properties of new lead halide perovskites which show promising performance in optoelectronic applications as long-wave infrared detectors and thermoelectrics. Our results provide evidence that the band gap of these compounds can be tuned upon the introduction of appropriate superalkali moieties at the cationic A-sites in the CsPbI3-type structure. The computed band gap is 0.36 eV (direct) and 0.41 eV (indirect) for [Li3O]PbI3 and [Li3S]PbI3, respectively. By changing the chemical environment in the Pb-halide perovskite structure, we see drastic changes in the shape of both valence and conduction bands, as compared to CsPbI3. Introducing superalkali cations produces extra electronic states close to the Fermi level which arise from the formation of delocalized energy states, where a strong hybridization is identified between Pb and Li s-states near the top of the valence band. This can promote the hole mobility and increase the exciton diffusion length at longer wavelengths. Berry phase calculations show rather significant spontaneous polarization of 34 and 15 μC cm−2 along the x-axis in both [Li3O]PbI3 and [Li3S]PbI3, indicative of ferroelectric behavior.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...