A modeling study of methane hydrate decomposition in contact with the external surface of zeolites†
Abstract
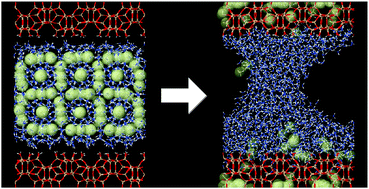
The behavior of methane hydrate (MH) enclosed between the (010) surfaces of the silicalite-1 zeolite was studied by means of molecular dynamics simulations at temperatures of 150 and 250 K. Calculations reveal that the interaction with the hydrophilic surface OH groups destabilizes the clathrate structure of hydrate. While MH mostly conserves the structure in the simulation at the low temperature, thermal motion at the high temperature breaks the fragilized cages of H-bonded water molecules, thus leading to the release of methane. The dissociation proceeds in a layer-by-layer manner starting from the outer parts of the MH slab until complete hydrate decomposition. The released CH4 molecules are absorbed by the microporous solid, whereas water is retained at the surfaces of hydrophobic silicalite and forms a meniscus in the interlayer space. Methane uptake reaches 70% of the silicalite sorption capacity. The energy necessary for the endothermic MH dissociation is supplied by the exothermic methane absorption by the zeolite.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...