The influence of carbon concentration on the electronic structure and magnetic properties of carbon implanted ZnO thin films†
Abstract
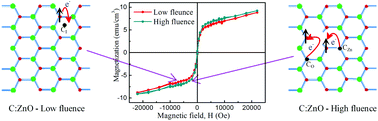
The influence of carbon concentration on the electronic and magnetic properties of C-implanted ZnO thin films has been studied using synchrotron radiation based X-ray absorption spectroscopic techniques and vibrating sample magnetometer measurements. 20 keV carbon ions were implanted in ZnO films with different fluences (2 × 1016, 4 × 1016 and 6 × 1016 ions per cm2). The pristine ZnO film shows diamagnetic behaviour while the C-implanted films exhibit room temperature ferromagnetism. Our first-principles calculations based on density functional theory show an appreciable magnetic moment only when the implanted C atom sits either in the O-site (2 μB) or in the interstitial position (1.88 μB), whereas the C atom in the Zn substitutional position does not possess any magnetic moment. X-ray absorption near edge structure analysis at the O K-edge reveals that the charge transfer from O-2p to the C-defect site causes the ferromagnetism in the C-implanted ZnO film at low fluence. However at high fluence, the implanted C replaces the lattice and produces more Zn vacancies, as evidenced by extended X-ray absorption fine structure studies at the Zn K-edge, which favors the ferromagnetism. The persistence of the implanted carbon and ferromagnetism of the C-implanted ZnO film has also been studied by isothermal annealing at 500 °C and discussed in detail.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...