Reduction and oxidation of Au adatoms on the CeO2(111) surface – DFT+U versus hybrid functionals†
Abstract
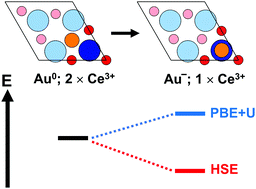
Recently we showed that Au atoms may titrate Ce3+ ions in near-surface layers of reduced CeO2(111). This surface contained oxygen vacancies in subsurface position within the topmost O–Ce–O trilayer [Pan et al., Phys. Rev. Lett., 2013, 111, 206101.]. The present work builds upon these findings and discusses additional results obtained using PBE+U and hybrid functionals. These approaches do not predict the same relative stabilities for the various adsorption sites of a single Au adatom at an O-defect concentration of a ¼ ML or 1.984 nm−2. We attribute this discrepancy to a different alignment within the O 2p–Ce 4f gap, i.e. a different order by energy of partially occupied Ce 4f and Au 6s orbitals. The energy offset of these orbitals matters, because the adsorption of Au0(6s1) atop Ce3+(4f1) or atop a subsurface oxygen atom in the first coordination shell of a Ce3+(4f1) involves creation of Au−(6s2) and Ce4+(4f0) ions. The electron transfer to Au is coupled to stabilizing ionic relaxation in the lattice, commonly known as polaronic distortion, reinforcing the Au–Ce bond. The order of 4f and 6s orbitals depends on the density functional approximation and is also strongly influenced by the oxygen defect concentration.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...