Hydrophobic hydration and anomalous diffusion of elastin in an ethanolic solution
Abstract
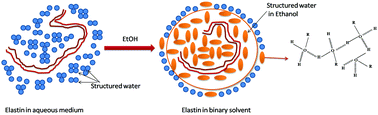
Elastin is an important structural protein that confers elasticity to tissues. It is widely used in the biosynthesis of human elastic tissues and exhibits interesting properties. This study reports an insight into the unusual dispersion and anomalous diffusion of elastin in an ethanolic solution. Due to its complex hydrophobic structure, its dispersibility was found to be sensitive towards the hydrophobicity of the solvent. Electrophoresis measurements (zeta-potential data) revealed that its net polarity changed from an anionic to a cationic state with the decreasing solvent hydrophobicity (ethanol content in the solvent). An interesting transition temperature of ∼297 K was observed above which the hydrophobic interactions among the protein molecules became dominant. Double-layer repulsion between protein molecules competes with attractive hydrophobic interactions and causes molecular self-organization. A DLVO-based theoretical model showed that hydrophobic interactions were facilitated by a binary solvent (ethanol–water), and the repulsive double layer screening provided sufficient energy to overcome the interactions between hydrophobic domains in the protein molecule and allow the self-assembly to occur.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...