Entropy in multiple equilibria, theory and applications†
Abstract
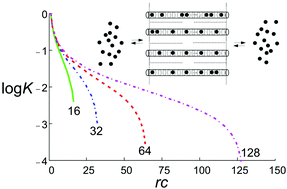
Analysis of multiple equilibria where the binding enthalpy of the species is the same for all sites and independent of those that are already bonded delivers insight on the evolution of the entropy as the reactions proceed and explains why the equilibrium constants always decrease with increasing number of occupied sites. The validity of the results is independent of the nature of bonding. Consequences are explained by discussing dicarboxylic acids, cation exchange of zeolite A, and the insertion of guests into the one-dimensional channels of zeolite L, by cation exchange for cationic guests and from the gas phase for neutral molecules. The quantitative link between the description of multiple equilibria and Langmuir's isotherm equation provides new insight. We express the concentration dependence of fraction filling of guests on the length of the channels, a result which is important for understanding observations and planning the synthesis of new host–guest composites. The free reaction enthalpy can be split in the particle distribution term and all other contributions. The results are therefore relevant for analyzing and interpreting experimental data also of systems where the condition of constant binding enthalpy is not or only partially fulfilled.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...