Negative thermal expansion in 2H CuScO2 originating from the cooperation of transverse thermal vibrations of Cu and O atoms
Abstract
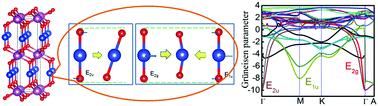
Negative thermal expansion (NTE) originating from the transverse thermal vibrations of metal atoms is seldom reported, which is why the transparent conducting oxide 2H CuScO2 is such a unique case. Using the density functional theory (DFT) and the quasi-harmonic approximation (QHA), the thermal properties of 2H CuScO2 were investigated. The coefficient of thermal expansion (CTE) and the Grüneisen parameters of different vibrational modes were calculated, and we found that, up to a temperature of 200 K, 2H CuScO2 displays a strong NTE behavior along the c-axis (i.e. along the O–Cu–O linkage), with an average CTE of approximately −2 × 10−6 K−1. Our calculations are consistent with the experimental values. Furthermore, we reveal that low energy modes (0–150 cm−1) originating from the cooperation of transverse vibrations of Cu and O atoms, which result in larger negative Grüneisen parameters and vibrational frequency softening phenomenon under pressure, are the main reasons for the NTE of such materials with a 2H structure. Our findings not only provide a better understanding of the NTE mechanism, but also present a report on detailed abnormal thermal properties in 2H CuScO2 that have applications in electronic, electrochemical and optoelectronic devices.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...