Simulation of selective thermodynamic deposition in nanoholes
Abstract
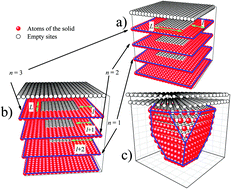
The deposition of particles in nanoholes is analyzed, taking into account the curvature of their inner walls. Different lattice-gas models of the nanoholes are considered. The heterogeneous surface are shaped from a (100)-surface where a nanohollow are incorporated with parallelepiped or polyhedral geometry. Several deposition stages are identified as a function of the degree of curvature of the inner walls of the nanoholes. The Monte Carlo technique in the grand canonical ensemble is used to calculate isotherms, isosteric heats, energies per site and other thermodynamic properties. This study is based on different magnitudes of the interaction energies between the particles being deposited and those surrounding the nanohole.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...