Hydration in silica based mesoporous materials: a DFT model†
Abstract
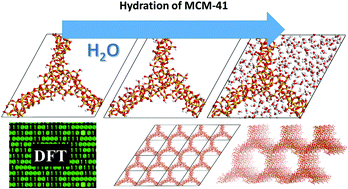
The MCM-41 material is very commonly used as a support for catalysts. However, theoretical investigations are significantly limited due to the lack of appropriate models that well and accurately describe the real material and enable effective computation at the same time. In this work, our aim is to obtain calculable models at the DFT level of MCM-41 which are as close as possible to the real material. In particular the hydration degree has been investigated, and we present and characterize here for the first time a model for the MCM-41 unit cell filled with explicit solvent water molecules. This is particularly important, because the models developed here are aimed to be further applied in theoretical ab initio/DFT studies of adsorption or as a support for modelling active sites in catalysts.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...