Global optimization of small bimetallic Pd–Co binary nanoalloy clusters: a genetic algorithm approach at the DFT level†
Abstract
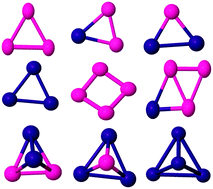
The global optimisation of small bimetallic PdCo binary nanoalloys are systematically investigated using the Birmingham Cluster Genetic Algorithm (BCGA). The effect of size and composition on the structures, stability, magnetic and electronic properties including the binding energies, second finite difference energies and mixing energies of Pd–Co binary nanoalloys are discussed. A detailed analysis of Pd–Co structural motifs and segregation effects is also presented. The maximal mixing energy corresponds to Pd atom compositions for which the number of mixed Pd–Co bonds is maximised. Global minimum clusters are distinguished from transition states by vibrational frequency analysis. HOMO–LUMO gap, electric dipole moment and vibrational frequency analyses are made to enable correlation with future experiments.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...