Effects of temperature, salt concentration, and the protonation state on the dynamics and hydrogen-bond interactions of polyelectrolyte multilayers on lipid membranes
Abstract
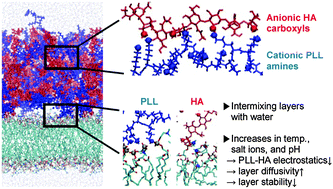
Polyelectrolyte multilayers, which consist of poly-L-lysines (PLL) and hyaluronic acids (HA), are simulated on phospholipid membranes with explicit water at different temperatures, salt concentrations, and protonation states of PLL that correspond to pH 7 or higher. PLL and HA polymers, which are initially sequentially deposited as three HA/PLL bilayers above the membrane, partially intermix with each other within 300 ns, and with a significant amount of water at almost half of its bulk density. With reduced protonation of amine groups of PLL, the polymers diffuse faster, especially at higher temperatures, and for 0%-protonation, disperse into the water, due to the many fewer hydrogen bonds between PLL and HA polymers. When PLL is protonated, the addition of salt ions weakens electrostatic interactions between PLL and HA and, at 0.5 M NaCl, eventually reduces the number of hydrogen bonds, which in experiments leads to hole formation inside the PLL/HA film. Multilayers are stabilized by hydrogen bonds, primarily between charged groups and to a lesser extent between uncharged groups. PLL and HA also electrostatically interact with lipid head groups of membranes which reduces the lateral mobility of membrane lipids, to an extent dependent on the salt concentration. These findings help quantitate the effects of temperature, salt, and the protonation state (or pH) on the stability and dynamics of multilayers and membranes, and show trends that compare favorably with the experimental observations of the swelling of multilayers.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...