Adsorption according to the Langmuir–Freundlich model is the detection mechanism of the antigen p53 for early diagnosis of cancer
Abstract
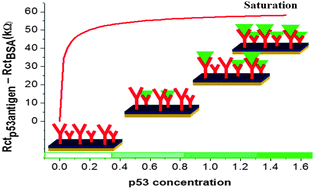
Biosensors for early detection of cancer biomarkers normally depend on specific interactions between such biomarkers and immobilized biomolecules in the sensing units. Though these interactions are expected to yield specific, irreversible adsorption, the underlying mechanism appears not to have been studied in detail. In this paper, we show that adsorption explained with the Langmuir–Freundlich model is responsible for detection of the antigen p53 associated with various types of cancers. Irreversible adsorption was proven between anti-p53 antibodies immobilized on the biosensors and the antigen p53, with the adequacy of the Langmuir–Freundlich model being confirmed with three independent experimental methods, viz. polarization-modulated infrared reflection absorption spectroscopy (PM-IRRAS), nanogravimetry using a quartz crystal microbalance and electrochemical impedance spectroscopy. The method based on this irreversible adsorption was sufficiently sensitive (limit of detection of 1.4 pg mL−1) for early diagnosis of Hodgkin lymphoma, pancreatic and colon carcinomas, and bladder, ovarian and lung cancers, and could distinguish between MCF7 cells containing the antigen p53 from Saos-2 cells that do not contain it.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...