A study of the interfacial resistive switching mechanism by proton exchange reactions on the SiOx layer
Abstract
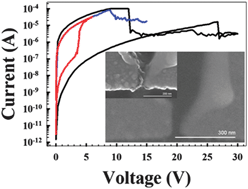
In this work, we investigated SiOx-based interfacial resistive switching in planar metal–insulator–metal structures using physical/chemical/electrical analyses. This work helps clarify the interfacial reaction process and mechanism in SiOx, and also shows the potential for high temperature operation in future nonvolatile memory applications.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...