Intensified effects of multi-Cu modification on the electronic properties of the modified base pairs containing hetero-ring-expanded pyrimidine bases†
Abstract
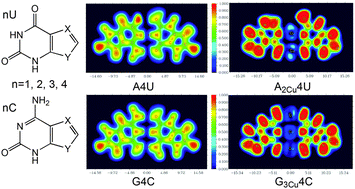
Novel DNA base pair derivatives (A2CunU, A2CunC, G3CunU, and G3CunC) are designed by aromatic expansion of pyrimidine bases with four kinds of hetero-rings (denoted by nC and nU, n = 1, 2, 3, and 4) and metal-decoration through Cu replacement of hydrogens in the Watson–Crick hydrogen bond region. Their structures and properties are calculated for examining the cooperative effects of the two modification ways. The calculated results reveal that multiple Cu decoration makes up the deficiencies of size-expansion, and exhibits not only increase of structural stability and reduction of ionization potentials, but also ideal shrink of the HOMO–LUMO gaps, notable enhancement of interbase coupling as well as remarkable redshifts of π → π* transitions for all M-x modified base pairs. The decrease extents of the gaps and ionization potentials follow the same order G3CunU > G3CunC > A2CunU > A2CunC, and in each series (denoted by different n), the gaps, ionization potentials and first π → π* transition energies have an order of 4 < 1 < 2 < 3. The Cu d orbitals function as bridges for π electron delocalization on the conjugated aromatic rings of two bases, leading to an enhancement of transverse electronic communication, as verified by spin density delocalization, orbital composition changes, redshift of the π → π* transition and also advocated by the electron-sharing indexes such as delocalization index, Mayer bond orders and multicenter bonding. Electron localization function ELF-π isosurfaces above the molecular plane further suggested that effective longitudinal conduction is closely relevant with the bicyclic domain involving good electron delocalization and strong π–π stacking between layers. This work presents theoretical evidence for the cooperative effects of metal decoration and ring-expansion modifications on the electronic properties of the modified base pairs and also proves that the base pairs designed here could be competent building blocks for the DNA-based nanowires with improved electron activity and excellent conductivity.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...