X-ray diffraction and high-resolution TEM observations of biopolymer nanoskin-covered metallic copper fine particles: preparative conditions and surface oxidation states
Abstract
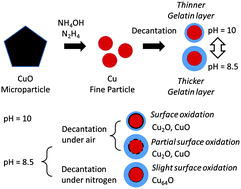
Metallic copper fine particles used for electro conductive pastes were prepared by the chemical reduction of cupric oxide microparticles in the presence of gelatin. After reduction, the fine particles were collected by decantation with pH control and washing, followed by drying at a moderate temperature. The surface oxidation state of the obtained copper fine particles could be considerably varied by altering the pH of the particle dispersion, as shown by X-ray diffraction and high-resolution transmission electron microscopy. Our results strongly indicate that decantation under a nitrogen atmosphere can prevent the oxidation of copper fine particles but a slight oxidation was found.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...