Bismuth and chromium co-doped strontium titanates and their photocatalytic properties under visible light irradiation†
Abstract
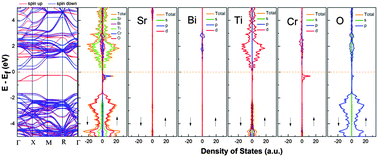
Modification of prototype perovskite compound SrTiO3 by introducing foreign elements has been an appealing means to endow this wide band gap semiconductor with visible light responses. Here we systematically investigated a series of Sr1−xBixTi1−xCrxO3 solid solution compounds prepared by two different synthetic routes, namely, solid state reactions and the hydrothermal method. Their crystal structures as well as other physicochemical properties were explored. Our results showed that a number of important factors such as microstructures, crystallinity, light absorbance and surface compositions etc. are all strongly correlated with the synthetic methods used. The hydrothermal method is generally helpful for morphology controls as well as avoiding Cr6+ defects and Sr segregation at the surface, thereby contributing to a high photocatalytic activity. Better performance normally occurs in samples with a high crystallinity and free of defects like Bi5+. Theoretical calculations suggest that Cr plays an important role in band gap reduction and photocatalytic reactions, while Bi only acts as a constituent cation for the perovskite structure and does not significantly alter the electronic structures near the Fermi level. Our findings have revealed how synthetic routes are relevant to the final photocatalytic properties of a compound, and therefore comparisons among various photocatalysts have to include concerns about their preparation history.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...