Vibronic bandshape of the absorption spectra of dibenzoylmethanatoboron difluoride derivatives: analysis based on ab initio calculations†
Abstract
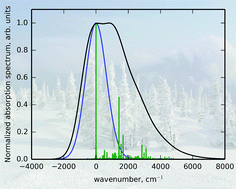
The nature of absorption bandshapes of dibenzoylmethanatoboron difluoride (DBMBF2) dye substituted in ortho-, meta-, and para-positions of the phenyl ring is investigated using DFT and TDDFT with the range-separated hybrid CAM-B3LYP functional and the 6-311G(d,p) basis set. The solvent effects are taken into account within the polarized continuum model. The vibronic bandshape is simulated using a time-dependent linear coupling model with a vertical gradient approach through an original code. For flexible chromophores, the spectra of individual conformers are summed up with Boltzmann factors. It is shown that the long-wavelength absorption bandshape of DBMBF2 derivatives is determined by three factors: the relative statistical weights of conformers with different electronic absorption patterns, the relative position and intensity of the second low-energy electronic transition, and the vibronic structure of individual electronic peaks. The latter is governed by the relationship between the hard vibrational modes, which contribute to vibronic progression, and soft modes, which provide broadening of the peaks. The simulated spectra of the dyes in the study are generally consistent with the available experimental data and explain the observed spectral features.


 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...