Functionalisation and immobilisation of an Au(110) surface via uracil and 2-thiouracil anchored layer
Abstract
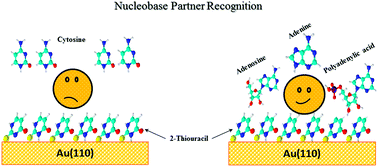
We study surface functionalisation by uracil and 2-thiouracil, and immobilisation of several DNA moieties on functionalised gold surfaces. The combination of X-ray photoelectron and near-edge X-ray absorption spectroscopy allowed us to obtain a complete understanding of complex interfacial processes, starting from adsorption of biomolecules onto the metallic surface and progressing towards a specific surface functionality for interactions with other biologically related adsorbates. Au(110) surfaces were functionalised by deposition of uracil and 2-thiouracil molecules under vacuum conditions, and then tested for their selectivity by immobilisation of different DNA moieties deposited from aqueous solutions. We observed that adenine, adenosine, and RNA polymer (polyadenylic acid) from saturated solutions were immobilized successfully on the 2-thiouracil, but those from dilute (1%) solutions were not. However, cytosine failed to adsorb even from saturated solution. The chemical states of the biologically related adsorbates were investigated and the geometrical orientation of uracil and 2-thiouracil on the Au(110) surface was determined using both spectroscopic techniques.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...