Hydration structure of strongly bound water on the sulfonic acid group in a Nafion membrane studied by infrared spectroscopy and quantum chemical calculation†
Abstract
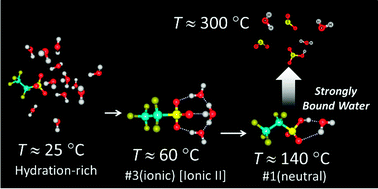
The hydration structure of the ‘strongly bound water’ around the sulfonic acid (SA) groups in Nafion, which has recently been revealed by 1H NMR spectroscopy (Anal. Chem., 2013, 85, 7581), is studied using infrared spectroscopy with the aid of quantum chemical (QC) calculations. During a heated drying process, bulky water is firstly dehydrated, which is followed by the disappearance of the hydronium ion and the appearance of bands that have been assigned to the fully dehydrated species at 140 °C. However, a spectral simulation based on QC reveals that the spectrum at 140 °C comes from the SA group associated with a single-water molecule via two H-bonds. This implies that a thoroughly dried membrane is unavailable even at 140 °C, and the involved water corresponds to the ‘strongly bound water.’ The QC-analytical results are experimentally confirmed by evolved gas analysis mass spectrometry (EGA-MS). At ca. 300 °C, which is the temperature where the SA group is selectively decomposed, the molecular fragment of SO2 is observed accompanying water molecules as expected. This confirms that the last single-water molecule can remain on the SA group until the thermal decomposition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...