A functionalised nickel cyclam catalyst for CO2 reduction: electrocatalysis, semiconductor surface immobilisation and light-driven electron transfer†
Abstract
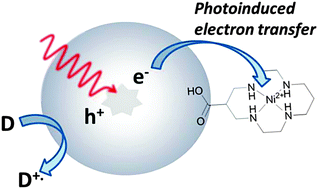
The immobilisation of electrocatalysts for CO2 reduction onto light harvesting semiconductors is proposed to be an important step towards developing more efficient CO2 reduction photoelectrodes. Here, we report a low cost nickel cyclam complex covalently anchored to a metal oxide surface. Using transient spectroscopy we validate the role of surface immobilisation on enhancing the rate of photoelectron transfer. Furthermore [Ni(1,4,8,11-tetraazacyclotetradecane-6-carboxylic acid)]2+ (2) is shown to be a very active electrocatalyst in solution.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...