Theoretical investigation on the mechanism and dynamics of oxo exchange of neptunyl(vi) hydroxide in aqueous solution†
Abstract
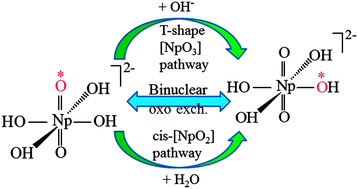
Four types of reaction mechanisms for the oxo ligand exchange of monomeric and dimeric neptunyl(VI) hydroxide in aqueous solution were explored computationally using density functional theory (DFT) and ab initio classical molecular dynamics. The obtained results were compared with previous studies on the oxo exchange of uranyl hydroxide, as well as with experiments. It is found that the stable T-shaped [NpO3(OH)3]3− intermediate is a key species for oxo exchange in the proton transfer in mononuclear Path I and binuclear Path IV, similar to the case of uranyl(VI) hydroxide. Path I is thought to be the preferred oxo exchange mechanism for neptunyl(VI) hydroxide in our calculations, due to the lower activation energy (22.7 and 13.1 kcal mol−1 for ΔG‡ and ΔH‡, respectively) of the overall reaction. Path II via a cis-neptunyl structure assisted by a water molecule might be a competitive channel against Path I with a mononuclear mechanism, owing to a rapid dynamical process occurring in Path II. In Path IV with the binuclear mechanism, oxo exchange is accomplished via the interaction between [NpO2(OH)4]2− and T-shaped [NpO3(OH)3]3− with a low activation energy for the rate-determining step, however, the overall energy required to fulfill the reaction is slightly higher than that in mononuclear Path I, suggesting a possible binuclear process in the higher energy region. The chemical bonding evolution along the reaction pathways was discussed by using topological methodologies of the electron localization function (ELF).

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...