The dynamic action mechanism of small cationic antimicrobial peptides
Abstract
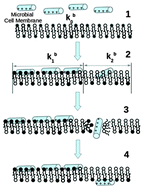
Antimicrobial peptides form part of the immune system as protection against the action of external pathogens. The differences that exist between mammalian and microbial cell membrane architectures are key aspects of the ability of these peptides to discriminate between pathogens and host cells. Given that the pathogen membrane is the non-specific target of these cationic peptides, different molecular mechanisms have been suggested to describe the rules that permit them to distinguish between pathogens and mammalian cells. In this context, and setting aside the old fashion idea that cationic peptides act through one mechanism alone, this work will provide insight into the molecular action mechanism of small antimicrobial peptides, based on molecular dynamics simulations of phospholipid bilayers that mimic different cell membrane architectures. After measuring different properties of these lipid bilayers, in the absence and presence of peptides, a four-step action mechanism was suggested on the basis of the formation of phospholipid rafts induced by the presence of these cationic peptides. Thus, this work shows how differences in the bending modulus (kb) of these lipid rafts and differences in the free energy profiles (ΔG(z)) associated with the insertion of these peptides into these lipid rafts are key aspects for explaining the action mechanism of these cationic peptides at the molecular level.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...