Effect of arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides on membrane pore formation and life-times: a molecular simulation study
Abstract
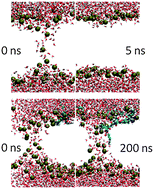
The molecular basis for the effectiveness of arginine-rich cell penetrating peptides (ARCPPs) traversing a cell membrane barrier is not well established. The fact that a threshold concentration of ARCPPs is required for efficient translocation in model membranes suggests cooperative action by ARCPPs. We used umbrella sampling simulations to calculate the free energies for membrane pore formation. Membrane-bound octaarginine (ARG8) peptides showed little cooperativity in lowering the free energy barrier to generate membrane pores by direct peptide translocation or by lipid flip-flop. Instead, high concentrations of ARG8 peptides were found to expand the surface area of the lipid bilayer due to the deep partitioning of guanidinium ions into the lipid glycerol regions. Surface-bound ARG8 peptides can also insert an arginine side chain into one existing transient membrane pore, and the lifetime of the transient membrane pore is significantly extended by arginine. This suggests a cooperative kinetic mechanism may act above a threshold adsorption concentration to facilitate the rapid uptake of these peptides.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...