Gas-surface reactions of nitrate radicals with vinyl-terminated self-assembled monolayers†
Abstract
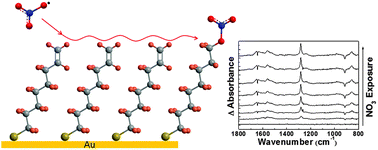
Interfacial reactions between gas-phase nitrate radicals, a key nighttime atmospheric oxidant, and a model unsaturated organic surface have been investigated to determine the reaction kinetics and probable reaction mechanism. The experimental approach employs in situ reflection-absorption infrared spectroscopy (RAIRS) to monitor bond rupture and formation while a well-characterized effusive flux of NO3 impinges on the organic surface. Model surfaces are created by the spontaneous adsorption of vinyl-terminated alkanethiols (HS(CH2)16CHCH2) onto a polycrystalline gold substrate. The H2C![[double bond, length as m-dash]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_e001.gif) CH-terminated self-assembled monolayers provide a well-defined surface with the double bond positioned precisely at the gas-surface interface. The surface reaction kinetics obtained from RAIRS revealed that the consumption rate of the terminal vinyl groups is nearly identical to the formation rate of a surface-bound nitrate species and implies that the mechanism is one of direct addition to the vinyl group rather than hydrogen abstraction. Upon nitrate radical collisions with the surface, the initial reaction probability for consumption of carbon–carbon double bonds was determined to be (2.3 ± 0.5) × 10−3. This reaction probability is approximately two orders of magnitude greater than the probability of ozone reactions on the same surface, which suggests that oxidation of surface-bound vinyl groups by nighttime nitrate radicals may play an important role in atmospheric chemistry despite their relatively low concentration.
CH-terminated self-assembled monolayers provide a well-defined surface with the double bond positioned precisely at the gas-surface interface. The surface reaction kinetics obtained from RAIRS revealed that the consumption rate of the terminal vinyl groups is nearly identical to the formation rate of a surface-bound nitrate species and implies that the mechanism is one of direct addition to the vinyl group rather than hydrogen abstraction. Upon nitrate radical collisions with the surface, the initial reaction probability for consumption of carbon–carbon double bonds was determined to be (2.3 ± 0.5) × 10−3. This reaction probability is approximately two orders of magnitude greater than the probability of ozone reactions on the same surface, which suggests that oxidation of surface-bound vinyl groups by nighttime nitrate radicals may play an important role in atmospheric chemistry despite their relatively low concentration.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...