Demixing and crystallization of DODAB in DPPC–DODAB binary mixtures
Abstract
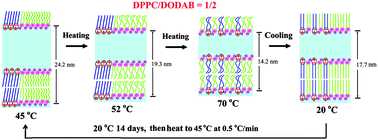
The crystallization mechanism of one lipid component within multicomponent lipid mixtures remains unclear. To shed light on this issue, we studied the demixing and crystallization behaviors of a binary lipid system using neutral dipalmitoylphosphatidylcholine (DPPC) and cationic dioctadecyldimethylammonium bromide (DODAB) as model molecules. The results indicate that when DODAB is no more than equimolar (e.g., DPPC/DODAB = 2/1 and 1/1), DPPC is miscible with DODAB and hinders the crystallization of DODAB, and the samples undergo reversible gel–fluid phase transitions upon heating and cooling. However, when DODAB is dominant in the mixture (DPPC/DODAB = 1/2), cooling of the mixed fluid phase results in the formation of a DODAB-rich gel domain and a DPPC–DODAB mixed gel domain. Such phase-separated mixed gels can undergo further demixing and crystallization, producing a DODAB-rich crystalline domain and a DPPC-rich tilted gel domain upon prolonged (or plus low-temperature) incubation. Besides, evidence has been given that the crystallized DODAB-rich domain remains in the same lipid bilayer as the DPPC-rich domain. All the three binary lipid mixtures can hold large amounts of water in the lipid interlamellar regions, allowing the incorporation of a large number of water-soluble substances such as DNA or proteins, which can be used for the fabrication of functional biofilms and biomaterials. Influences of water content and salt concentration on the phase structures (e.g., repeat distances) of the binary mixtures have also been studied.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...