Enhanced anomalous Hall effect in Fe nanocluster assembled thin films†
Abstract
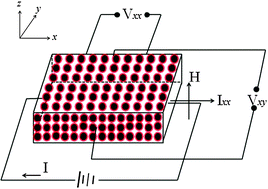
An enhanced anomalous Hall effect is observed in heterogeneous uniform Fe cluster assembled films with different film thicknesses (ta = 160–1200 nm) fabricated by a plasma-gas-condensation method. The anomalous Hall coefficient (Rs) at ta = 1200 nm reaches its maximum of 2.4 × 10−8 Ω cm G−1 at 300 K, which is almost four orders of magnitude larger than bulk Fe. The saturated Hall resistivity (ρAxy) first increases and then decreases with the increase of temperature accompanied by a sign change from positive to negative. Analysis of the results revealed that ρAxy decreases with increasing longitudinal resistivity (ρxx) on a double-logarithmic scale and obeys a new scaling relation of log(ρAxy/ρxx) = a0 + b0 log ρxx.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...