A conformation-selective IR-UV study of the dipeptides Ac-Phe-Ser-NH2 and Ac-Phe-Cys-NH2: probing the SH⋯O and OH⋯O hydrogen bond interactions†
Abstract
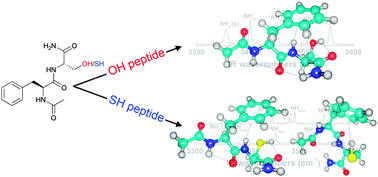
The conformational preferences of peptides are mainly controlled by the stabilizing effect of intramolecular interactions. In peptides with polar side chains, not only the backbone but also the side chain interactions determine the resulting conformations. In this paper, the conformational preferences of the capped dipeptides Ac-Phe-Ser-NH2 (FS) and Ac-Phe-Cys-NH2 (FC) are resolved under laser-desorbed jet cooling conditions using IR-UV ion dip spectroscopy and density functional theory (DFT) quantum chemistry calculations. As serine (Ser) and cysteine (Cys) only differ in an OH (Ser) or SH (Cys) moiety; this subtle alteration allows us to study the effect of the difference in hydrogen bonding for an OH and SH group in detail, and its effect on the secondary structure. IR absorption spectra are recorded in the NH stretching region (3200–3600 cm−1). In combination with quantum chemical calculations the spectra provide a direct view of intramolecular interactions. Here, we show that both FS as FC share a singly γ-folded backbone conformation as the most stable conformer. The hydrogen bond strength of OH⋯O (FS) is stronger than that of SH⋯O (FC), resulting in a more compact gamma turn structure. A second conformer is found for FC, showing a β turn interaction.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...