Conformational interchange of a carbohydrate by mechanical compression at the air–water interface†
Abstract
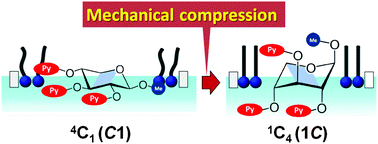
Methyl xylopyranoside containing three 4-(pyrene-1-yl)benzoyl groups (PyXy) undergoes conformational interchange within a Langmuir monolayer upon mechanical compression. This xylose-type molecular machine PyXy was immobilized within two different matrix lipids, methyl stearate and methyl 2,3,4-tri-O-stearoyl-β-D-xylopyranoside, which respectively form rigid and soft monolayers. Structural properties of the monolayer were characterized by assessing the compressibility, compression modulus, and ideal limiting molecular area of PyXy, all of which were estimated from the π–A isotherm measurements. Only the rigid monolayer exhibited a transition to the condensed phase with a limiting molecular area of PyXy smaller than that of the cross-sectional area of the xylopyranose ring in its C1 chair conformation. This suggests conformational interchange of PyXy from the most stable 4C1 (C1) form to the metastable 1C4 (1C) form. Surface-reflective fluorescence spectroscopy of the monolayer was applied to detect excimer emission resulting from the face-to-face dimerization of pyrenes attached at the O-2 and O-4 positions of xylose. Fluorescence intensity of the excimer increased abruptly in the condensed region only when the rigid monolayer was applied. These results indicate that the rigidity of the matrix monolayer is a critical aspect of the precise manipulation of molecular machines at interfaces. Consequently, this study demonstrates that including a molecular machine into a rigid lipid matrix is a promising means for the preparation of a novel nanoassembly with dynamic functionalities variable depending on a mechanical stimulus.
- This article is part of the themed collection: Mechanical properties of nanoassemblies

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...