Effect of cations on condensation of a mesogenic amphiphilic molecule at the air–aqueous electrolyte interface†
Abstract
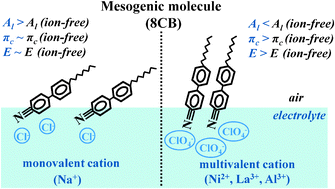
We report the interactions of a mesogenic molecule, 4′-octyl-4-biphenyl-carbonitrile (8CB), with some cations (Na+, Cu2+, Ni2+, La3+ and Al3+) dissolved in the aqueous subphase. Surface manometry studies show that the di- (Ni2+ and Cu2+) and trivalent (La3+) ions promote condensation in the area per molecule and enhance the stability of the monolayer. This is inferred from the increase in the values of collapse pressure and the compression elastic modulus. The specific ion effect is seen between perchlorate and chloride anions with respect to the Al3+ cation. The presence of monovalent ions (Na+) in the subphase does not influence the isotherm of 8CB. However, in this case, with pH (>6), the isotherm shifts to a higher area per molecule. The excess Gibbs free energy calculated for the 8CB monolayer indicates repulsive interaction for monovalent ions and attractive interaction for multivalent ions in the subphase. Kinetic studies of the monolayer in an ion-enriched subphase have yielded an additional characteristic time constant indicative of reorganization of the monolayer. Ellipsometric adsorption isotherm measurements carried out for representative ions show a reduction in the value of the ellipsometric angle with increasing valency. Our studies indicate that the interaction of ions with the 8CB monolayer at the air–electrolyte interface can be promoted by choosing cations of higher valency and anions of larger size, higher polarizability and chaotropic nature. These factors play an important role and can potentially affect the anchoring transition.

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...