Branched TiO2 nanoarrays sensitized with CdS quantum dots for highly efficient photoelectrochemical water splitting†
Abstract
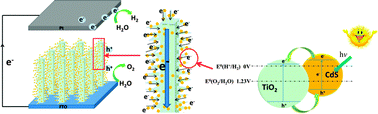
This paper describes the design, characterization, and utilization of branched TiO2 nanoarrays sensitized with CdS
- This article is part of the themed collection: Interfacial Phenomena in (De)hydrogenation Reactions

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...