Protonation equilibrium of the poly(allylammonium) cation in an aqueous solution of binary 1 : 1 electrolytes
Abstract
The (de)protonation equilibrium of the poly(allylammonium) 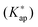 and concentration apparent equilibrium deprotonation constants (Kap) were calculated from the experimentally collected data and concentration profiles of dissociated and undissociated functional groups were obtained. The standard pK value of monomers was estimated by extrapolating the pKap values determined at various concentrations of added electrolyte to the degree of dissociation α = 1. The dependence of pKap on the degree of dissociation could be well described by the two parameter model according to Mandel. The variation of
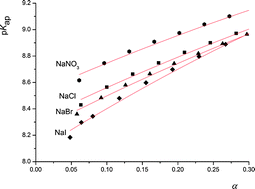
and concentration apparent equilibrium deprotonation constants (Kap) were calculated from the experimentally collected data and concentration profiles of dissociated and undissociated functional groups were obtained. The standard pK value of monomers was estimated by extrapolating the pKap values determined at various concentrations of added electrolyte to the degree of dissociation α = 1. The dependence of pKap on the degree of dissociation could be well described by the two parameter model according to Mandel. The variation of 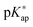 with monomer dissociation degree was found to be in satisfactory agreement with the cylinder Stern model, based on the Poisson–Boltzmann (PB) equation, and a constant Stern capacitance. Generally, the derived apparent constants showed a pronounced dependence on the concentration of binary electrolytes and a weak dependence on the type of anion counterbalancing the polyion charge. The influence of the PAH chain length (
with monomer dissociation degree was found to be in satisfactory agreement with the cylinder Stern model, based on the Poisson–Boltzmann (PB) equation, and a constant Stern capacitance. Generally, the derived apparent constants showed a pronounced dependence on the concentration of binary electrolytes and a weak dependence on the type of anion counterbalancing the polyion charge. The influence of the PAH chain length (

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...