Application of a contact mode AFM for spatially resolved electrochemical impedance spectroscopy measurements of a Nafion membrane electrode assembly†
Abstract
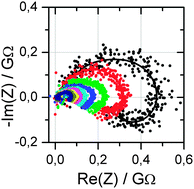
A Nafion
- This article is part of the themed collection: Electrified surface chemistry

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...