A new insight into the initial step in the Fischer–Tropsch synthesis: CO dissociation on Ru surfaces†‡
Abstract
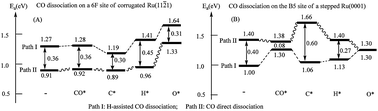
In the present work, we have investigated the CO dissociation on corrugated Ru(11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 1) and the stepped Ru(0001) surfaces by means of density functional theory with slab models. Our results show that, while the direct CO dissociation is preferred on the six-fold site of Ru(11
1) and the stepped Ru(0001) surfaces by means of density functional theory with slab models. Our results show that, while the direct CO dissociation is preferred on the six-fold site of Ru(11![[2 with combining macron]](https://www.rsc.org/images/entities/char_0032_0304.gif) 1), the H-assisted CO dissociation is found to be favored on the B5 site of the stepped Ru(0001) surface. Furthermore, we have studied the effects of co-adsorbed spectator species on the CO dissociation mechanisms. Our results demonstrate that spectators can change the potential energy landscape dramatically, such that different reaction mechanisms can be favored in the presence of different spectators. Neither the H-assisted CO dissociation mechanism nor the CO direct dissociation mechanism should be overlooked at authentic ambient conditions. This work emphasizes a dynamic picture of the reaction mechanisms due to the inherent structural and compositional inhomogeneity on surfaces. Different mechanisms can work together as different active sites will co-exist on a real
1), the H-assisted CO dissociation is found to be favored on the B5 site of the stepped Ru(0001) surface. Furthermore, we have studied the effects of co-adsorbed spectator species on the CO dissociation mechanisms. Our results demonstrate that spectators can change the potential energy landscape dramatically, such that different reaction mechanisms can be favored in the presence of different spectators. Neither the H-assisted CO dissociation mechanism nor the CO direct dissociation mechanism should be overlooked at authentic ambient conditions. This work emphasizes a dynamic picture of the reaction mechanisms due to the inherent structural and compositional inhomogeneity on surfaces. Different mechanisms can work together as different active sites will co-exist on a real
- This article is part of the themed collection: Computational Catalysis and Materials for Energy Production, Storage and Utilization

 Please wait while we load your content...
Please wait while we load your content...